Table of Contents
You’re estimating setup costs, rent, licenses, and visas when someone mentions Dubai offers zero personal income tax for business owners. Surprised? Dubai is more than a luxury destination; it’s a rising global hub for entrepreneurs, offering business-friendly laws, strategic location, and modern infrastructure. But starting a business here isn’t plug-and-play between choosing a free zone or mainland, and understanding legal and visa requirements. One wrong move can be costly. Your first decision impacts everything from ownership to market access and getting it right is critical.
Why Start a Business in Dubai in 2025?
Dubai stands out as a premier destination for entrepreneurs and businesses aiming for rapid growth and global reach. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa offers direct access to over two billion consumers and seamless international trade through world-class ports and airports. The city’s business-friendly environment is underpinned by supportive government policies, 100% foreign ownership in most sectors, and streamlined company formation processes that remove much of the traditional red tape.
Dubai’s tax advantages are another major draw: here no personal income tax, no capital gains tax, and highly competitive or zero corporate tax rates in free zones, maximizing profitability for both businesses and their employees. Entrepreneurs also benefit from a diverse, skilled workforce and modern infrastructure, including advanced digital services, 5G connectivity, and innovation hubs that support every stage of business growth.
With a robust, diversified economy spanning technology, logistics, finance, tourism, and more. Dubai provides a fertile ground for new ventures and established companies alike. Government initiatives like the Golden Visa and funding programs further encourage investment and long-term success. For anyone looking to launch or expand a business, Dubai offers unmatched opportunity, efficiency, and a vibrant ecosystem designed for ambitious growth.
What Are the Legal Requirements to Start a Business in Dubai?
Understanding Dubai’s legal framework is essential for anyone looking to establish a business in the emirate. Compliance with local laws and regulations ensures smooth operations and protects your venture from legal complications
1. Trade Name Approval
You must select and register a unique trade name for your business, which serves as its public identity. The name must comply with the Department of Economic Development (DED) guidelines, avoiding offensive language, religious references, or duplication of existing names. The trade name must also reflect the legal structure (such as LLC or Sole Establishment). Only after trade name approval can you proceed to obtain your trade license.
2. Activity Classification
You must define your business activity—commercial, professional, or industrial—as this determines the type of license you need. Dubai recognizes over 2,000 business activities, and selecting the correct classification is essential for regulatory compliance. Some activities may require additional approvals from sector-specific authorities (e.g., healthcare, education)
3. Jurisdiction Selection
Dubai offers three main jurisdictions for business setup:
- Mainland: Allows trade across the UAE and internationally, regulated by the Department of Economy and Tourism.
- Free Zone: Offers tax incentives and 100% foreign ownership but restricts direct local trade within the UAE.
- Offshore: Suited for international business without a physical presence in the UAE.
Your choice affects ownership rules, operational scope, and regulatory obligations.
4. Legal Structure
You must select an appropriate legal structure for your business, such as:
- Sole Proprietorship: A business in the UAE owned and operated by a single individual, providing them ownership and complete control over all business decisions, while also holding them personally liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
- Partnership Company: A structure where two or more partners (typically UAE nationals) jointly own and operate the business, sharing profits, management duties, and bearing unlimited liability for the company’s obligations.
- LLC (Limited Liability Company): A flexible entity where shareholders’ liability is limited to their capital contribution, allowing for multiple owners and, in many sectors, 100% foreign ownership.
- Private ShareHolding Company: A company with at least two and up to 200 shareholders, whose shares are privately held and not offered to the public, with liability limited to the value of shares held.
- Public ShareHolding: A company whose shares are publicly traded on the stock exchange, requiring a minimum of ten founders and significant capital, with shareholder liability limited to their shareholding.
- Civil Company: A partnership structure for professionals (such as doctors, engineers, or consultants) who wish to practice their profession together, with liability distributed among partners as per agreement.
- Branch of GCC Companies: An extension of a company established in another GCC country, allowed to operate in Dubai under the parent company’s name and legal responsibility.
Where Should You Set Up? Mainland vs Free Zone vs Offshore
Choosing the right jurisdiction is a crucial step for any company planning to operate in Dubai, as it determines your business’s regulatory environment, market access, and operational flexibility. Dubai offers three main options: Mainland, Free Zone, and Offshore, each catering to different business needs and strategies. Understanding the distinctions between these zones will help you align your setup with your company’s goals and long-term vision.
Mainland
Setting up a business in the Dubai mainland allows companies to operate anywhere within the UAE and internationally, offering the broadest market access and the ability to bid for government contracts. Mainland companies are licensed by the Department of Economic Development (DED) and can engage in a wide range of business activities with fewer restrictions on office location or currency movement. Recent reforms have enabled 100% foreign ownership for most activities, eliminating the need for a local sponsor, though some sectors may still require Emirati participation. Mainland setups typically involve higher regulatory compliance and costs but provide unmatched operational flexibility and growth opportunities.
Freezone
Free zones are designated economic areas that offer significant advantages, including 100% foreign ownership, corporate tax exemptions, full repatriation of profits, and streamlined administrative processes. Each free zone is governed by its own authority and often caters to specific industries, providing tailored infrastructure and networking opportunities. However, free zone companies are generally restricted to conducting business within their zone or internationally and cannot trade directly with the UAE mainland market without appointing a local distributor or establishing a mainland branch. Office requirements are flexible, ranging from virtual desks to full office spaces within the free zone.
Offshore
Offshore companies are international business entities registered in special offshore jurisdictions such as JAFZA, RAK ICC, or Ajman Offshore. These companies are primarily used for asset protection, holding investments, and international trade, benefiting from zero corporate tax and confidentiality. Offshore entities cannot conduct any business activity within the UAE and are not permitted to lease office space or hire staff locally; their operations are limited to activities outside the country. Offshore setups are the most cost-effective option but are suitable only for businesses that do not require a physical presence or local market access.
| Feature | Mainland | Freezone | Offshore |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Up to 100% foreign (most activities) | 100% foreign ownership | 100% foreign ownership |
| Market Access | UAE-wide and international | Within free zone and international (not mainland) | Only outside UAE |
| Taxation | 9% corporate tax above AED 375,000 | 0% corporate tax (if conditions met) | 0% corporate tax |
| Office Requirement | Mandatory physical office in UAE | Office/flexi-desk within free zone | No physical office required |
| Business Activities | Broadest range, incl. government contracts | Restricted to free zone activities | Asset holding, international trade only |
| Setup Cost | Higher | Moderate | Lowest |
| Regulatory Body | Department of Economic Development (DED) | Free Zone Authority | Offshore Registry |
| Local Sponsor | Not required for most activities | Not required | Not required |
Who is Eligible to Start a Business in Dubai Under Current Regulations
Under current regulations, both UAE nationals and foreign investors are eligible to start a business in Dubai. Recent legal reforms have significantly expanded opportunities for foreigners, allowing 100% foreign ownership in a wide range of commercial and professional activities on the mainland, as well as in all free zones, without the need for a local Emirati sponsor. This means that entrepreneurs from anywhere in the world can establish and fully own their businesses in Dubai, provided they meet the licensing requirements and submit the necessary documents, such as valid passports, trade name approval, and tenancy contracts.
Eligibility is determined by the chosen business activity, legal structure, and jurisdiction, mainland, free zone, or offshore. While most sectors are open to full foreign ownership, some strategic or restricted industries may still require local participation or special approvals. Additionally, Emirati and GCC nationals residing in Dubai can qualify for home-based businesses and other special categories. In all cases, applicants must comply with the regulatory procedures, obtain the appropriate business license, and fulfill any sector-specific requirements set by the relevant authorities.
How to Start a Business in Dubai: Step-by-Step Legal Process
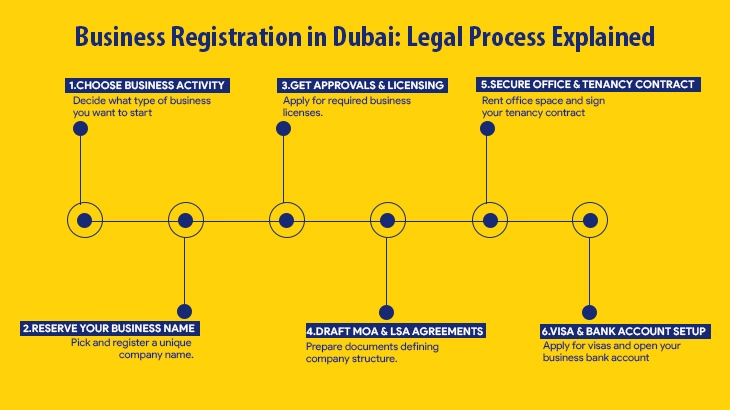
The legal process for starting a business in Dubai is structured and designed to ensure regulatory compliance at each stage. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the key legal steps required:
Step 1: Business Activity Selection
Begin by identifying your primary business activity, as this determines the type of license you will need for commercial, professional, industrial, or tourism. Dubai offers over 2,000 permitted activities, and your selection impacts regulatory requirements and approvals
Step 2: Name Reservation
Choose and reserve a unique trade name for your business that complies with Dubai’s naming regulations. The name must reflect your legal structure, avoid prohibited terms, and not duplicate existing names.
Step 3: Licensing (DED/Free Zone Authority)
Apply for the appropriate business license from the Department of Economy and Tourism (DET) for mainland setups or the relevant free zone authority. The license type must match your chosen business activity, and some sectors may require additional approvals from specialized government bodies.
Step 4: MOA & LSA Agreement
Draft and notarize the Memorandum of Association (MOA) for entities like LLCs or partnerships, and, if required, sign a Local Service Agent (LSA) agreement for businesses fully owned by non-GCC nationals. These documents define company ownership, management structure, and local representation.
Step 5: Office Space & Tenancy Contract
Secure a physical office or workspace that meets regulatory standards, and obtain a tenancy contract registered with the Ejari system (for mainland businesses). This address will be used for official correspondence and is a prerequisite for license issuance.
Step 6: Visa and Bank Account Setup
Once your company is licensed, you can apply for investor and employee visas as needed. Open a corporate bank account in Dubai to manage your business finances, providing all required company documents and identification for verification.
Common Mistakes New Entrepreneurs Make
New entrepreneurs in Dubai often make critical mistakes such as choosing the wrong business license or misunderstanding ownership rules, which can lead to operational delays, legal complications, or even financial penalties. Selecting the correct license whether commercial, professional, industrial, or tourism is essential, as each type is tailored for specific activities and comes with unique requirements and benefits. For example, a commercial license is ideal for trading businesses, while a professional license is necessary for service-based activities and allows for 100% foreign ownership in many cases.
Another common pitfall is not fully understanding the latest ownership regulations, especially with recent changes allowing full foreign ownership for most activities on the mainland and in free zones. Misinterpreting these rules can result in unnecessary partnerships or missed opportunities for full control over your business.
At Alhind BC, we guide you through each step helping you select the right license, understand the latest regulations, and ensure your business structure is fully compliant so you can avoid these costly mistakes and focus on growing your venture.
Success Tips from UAE Business Consultants
At Alhind Business Centre, our experience guiding entrepreneurs through Dubai’s dynamic business landscape has revealed key strategies for lasting success. First, always ensure thorough planning and compliance, understanding the latest regulations, choosing the right license, and selecting the optimal jurisdiction are critical for a smooth launch and sustainable growth. Our consultants emphasize the importance of tailored solutions: every business is unique, so we customize our approach to align with your specific goals, industry requirements, and future ambitions.
- Understand Regulatory Requirements: Stay updated on the latest UAE business laws, licensing regulations, and compliance standards to avoid costly mistakes and ensure a smooth setup process.
- Choose the Right Jurisdiction and License: Select the most suitable business zone (Mainland, Free Zone, or Offshore) and license type based on your activity and growth plans, as this impacts ownership, taxation, and market access.
- Leverage Expert Support: Work with experienced consultants like Alhind BC to navigate legal documentation, visa processing, and government approvals efficiently, saving you time and reducing stress.
- Prioritize Transparent Communication: Keep all stakeholders informed and maintain clear documentation at every stage to prevent misunderstandings and facilitate faster decision-making.
- Plan for Long-Term Growth: Consider scalability, office requirements, and future expansion when selecting your company structure and location, ensuring your business is set up for sustainable success.
- Build Strong Local Networks: Establish relationships with local partners, authorities, and service providers to access new opportunities and stay ahead of regulatory changes.
Why Choose Alhind for Business Setup in Dubai?
With a proven track record and deep expertise in Dubai’s business landscape, Alhind Business Centre stands out as a trusted partner for entrepreneurs and established companies alike. Our experienced team offers end-to-end support from company formation and licensing to visa processing and ongoing PRO services ensuring a seamless, compliant, and efficient setup process tailored to your unique needs. Clients consistently praise our responsive communication, transparent processes, and commitment to delivering fast, reliable results, making business setup stress-free and straightforward. Whether you’re launching a new venture or expanding into the UAE, Alhind BC’s personalized approach and industry knowledge help you realize your business ambitions with confidence.


















